Watch Live! China's Shenzhou 15 crew launches to Tiangong space station
Live: Special coverage of China's Shenzhou-15 manned space mission launch
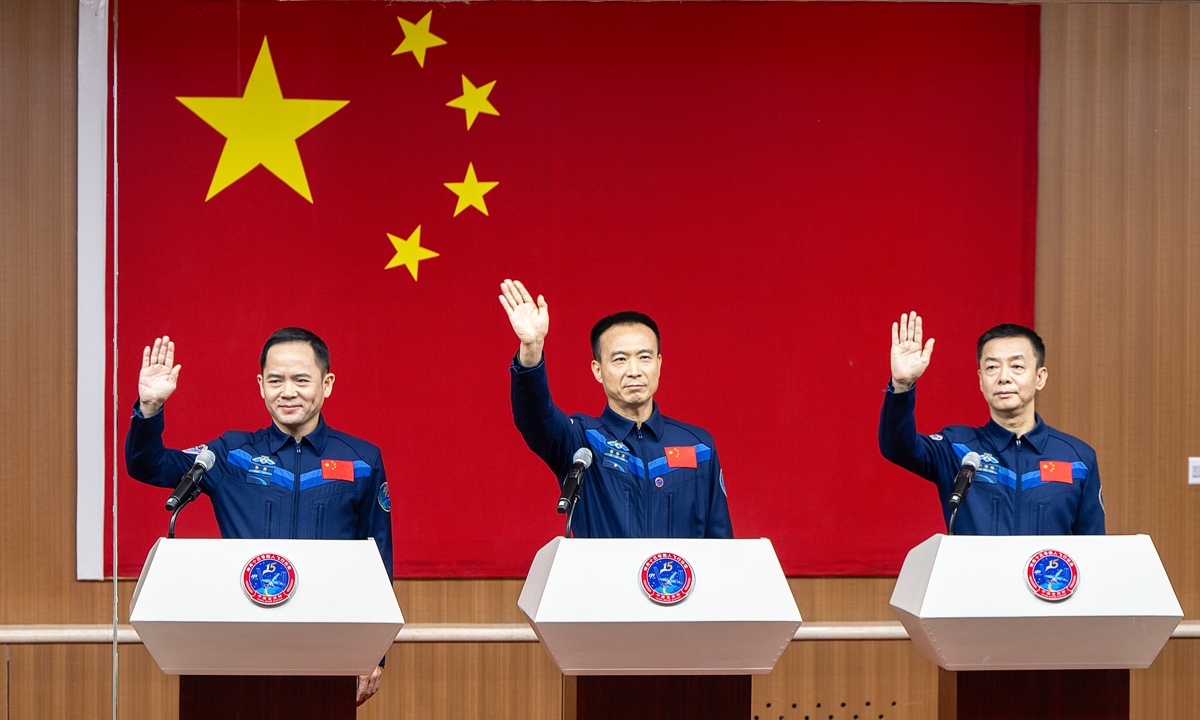 The line-up of three taikonauts for Shenzhou-15 manned spaceflight mission, Zhang Lu, Fei Junlong, and Deng Qingming (from left to right). Photo: VCG
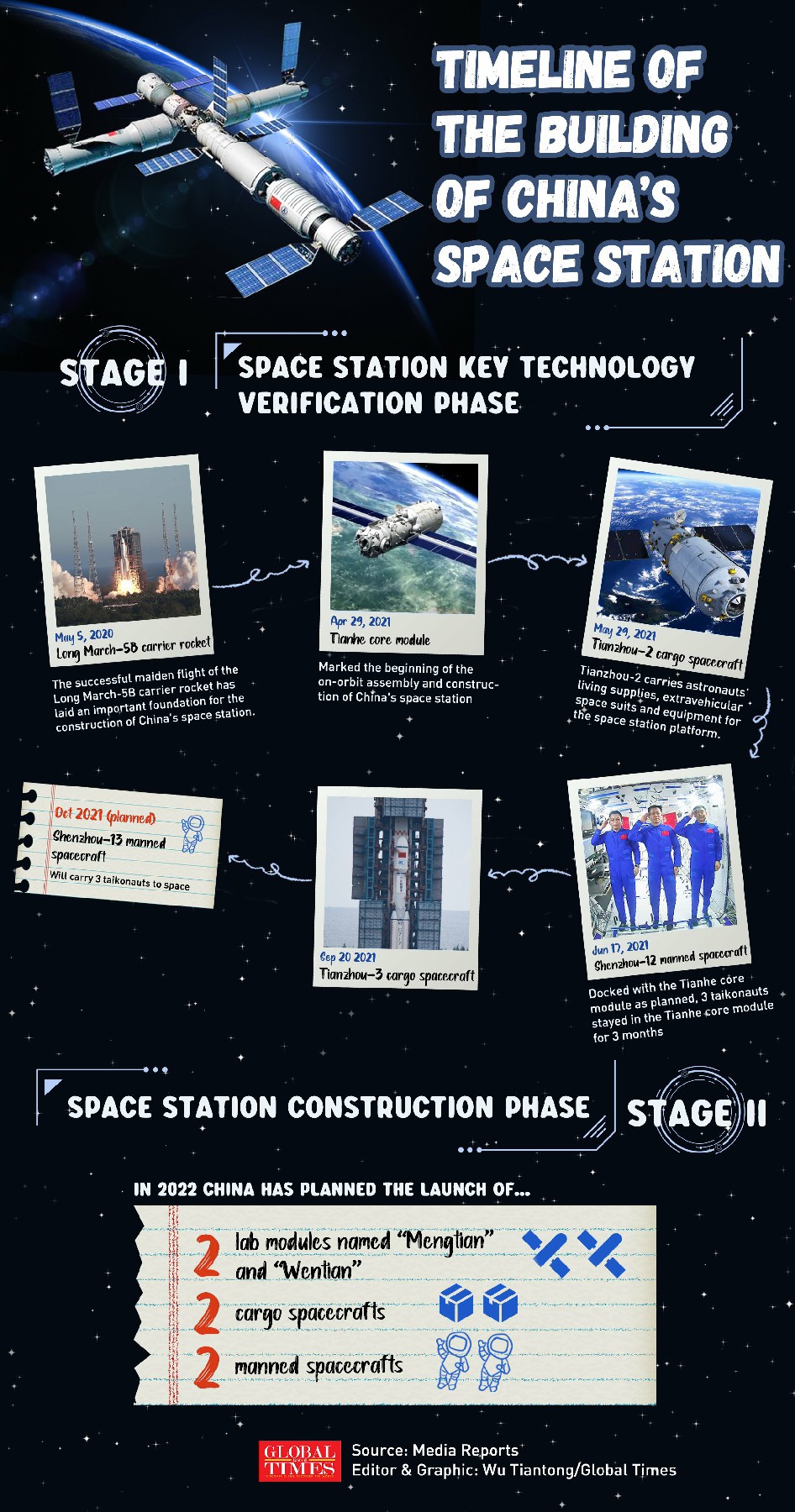
China on Monday unveiled the line-up of three taikonauts for Shenzhou-15 manned spaceflight mission that is set to be launched on Tuesday night. The trio led by mission commander Fei Junlong with two space newcomers Deng Qingming and Zhang Lu are going to conduct a direct handover in orbit with the Shenzhou-14 crew at the China Space Station in construction, which shall mark a first in China's aerospace history.
The upcoming Shenzhou-15 crewed spaceflight mission is not only the anchor-leg launch mission at the China Space Station construction stage, but also is the first one to embark on the next operational stage, Fei, the 57-year-old veteran taikonaut who visited the space as the mission commander in the China's Shenzhou-6 mission in 2005, remarked at a press conference on Monday at the Jiuquan Satellite Space Launch Center in Northwest China's Gansu Province.
The crew will carry out more experiments in orbit, operate, maintain and repair relevant equipment and above all execute even more challenging extravehicular activities, or known as spacewalks, with more complicated paths to take on, Fei said on Monday.
The Shenzhou-15 crew has undergone great amount of specific training, which made them very confident to deliver all the set goals and to successfully complete their space run, Fei said.
Deng Qingming, 56, is among the first batch of taikonauts trained in China that includes the country's first astronaut Yang Liwei and also his mission commander Fei in the Shenzhou-15 mission. He has served as a backup for nearly 25 years, in missions such as the Shenzhou-9 and 10, but never got the chance to fly. This will be his first time ever in space.
Zhang Lu, 46, also a new face, was selected in the second batch of taikonauts trained in China in 2010.
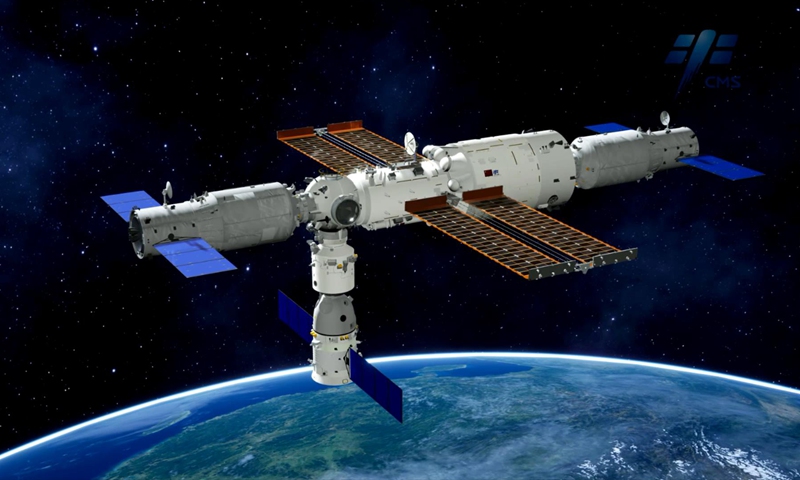
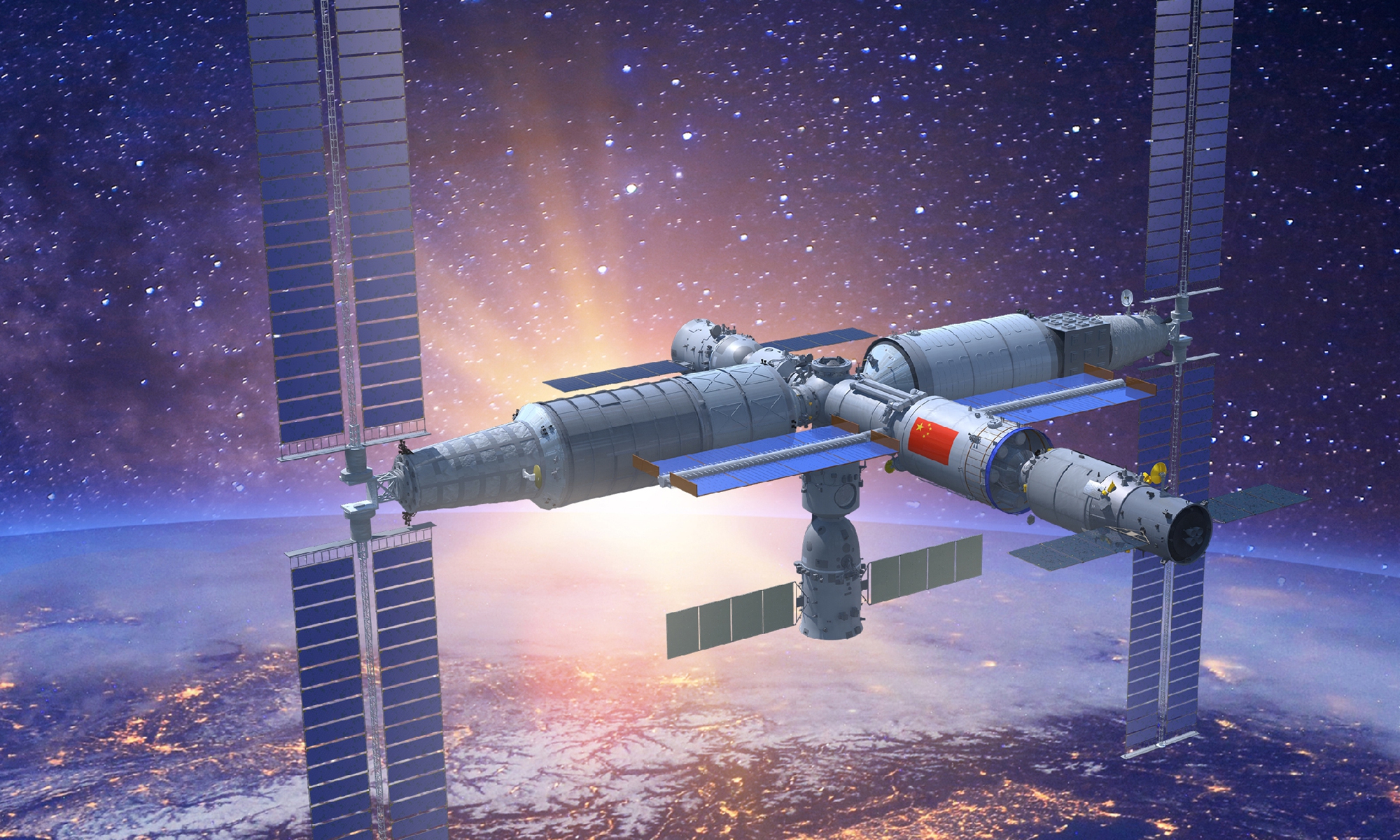
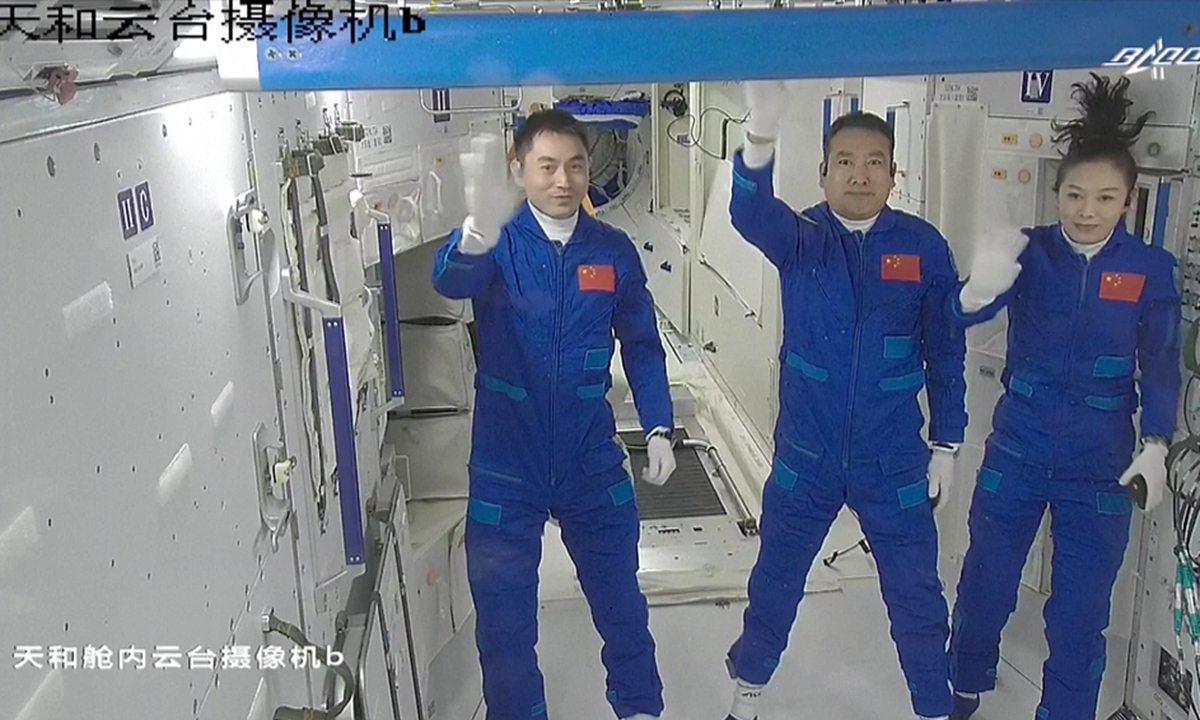
Mission insiders told the Global Times on Monday that the two crews of six taikonauts will carry out the space station handover in a face-to-face manner for the first time in the country's manned space history and that is not only of symbolic significance but also carries great practical values to the overall development of the country's first permanent space outpost.
Sources with China's astronaut training system, told the Global Times on Monday that such feat would enable the predecessor Shenzhou-14 to introduce and share what their work and life would be like inside the space station with the new Shenzhou-15 crew directly, boosting the continuity and efficiency of the handover.
It would also help save the resources to set the space station combo from occupied state to unoccupied one and then back again. And the handover will be more target-oriented, especially for those ongoing experiments and space station maintenance work, the sources said.
Having six taikonauts simultaneously onboard the China Space Station in construction, would also verify its performance under the full load condition, which would lay groundwork for future tasks where more payload technicians are needed for more complicated experiments, Song Zhongping, a space watcher and TV commentator, told the Global Times.
By plan, the handover will last for a week or so, and after that, Shenzhou-14 crew will return to the Dongfeng landing site on Earth.
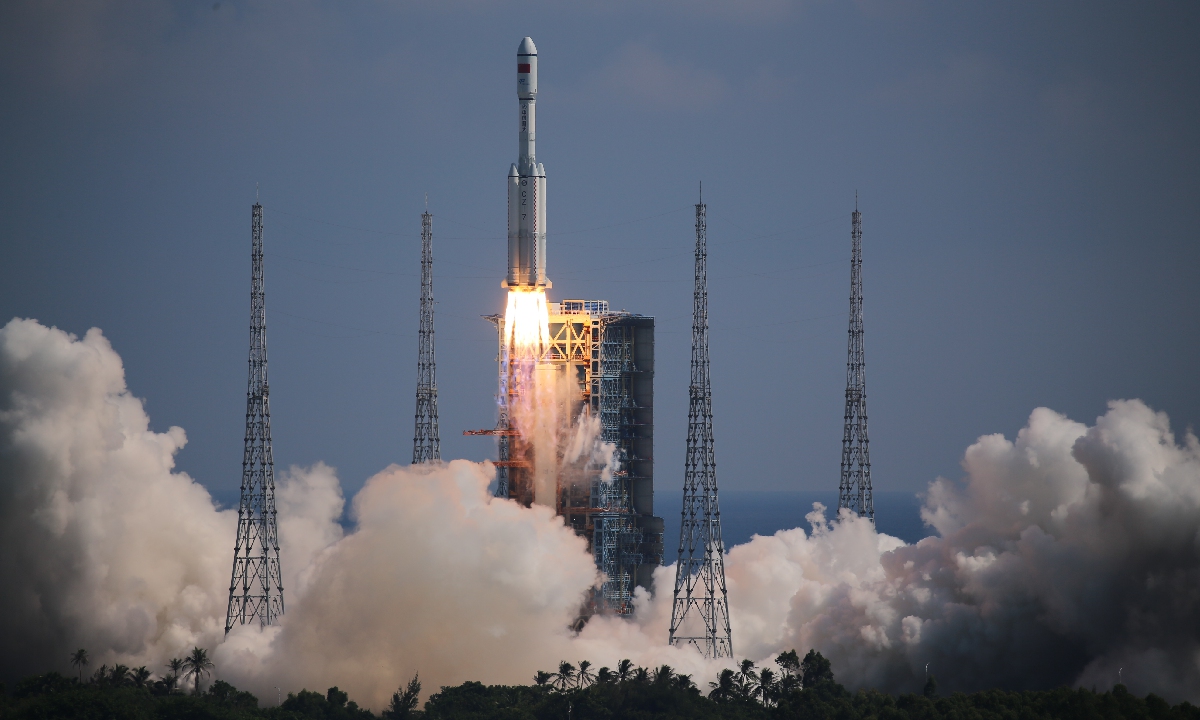
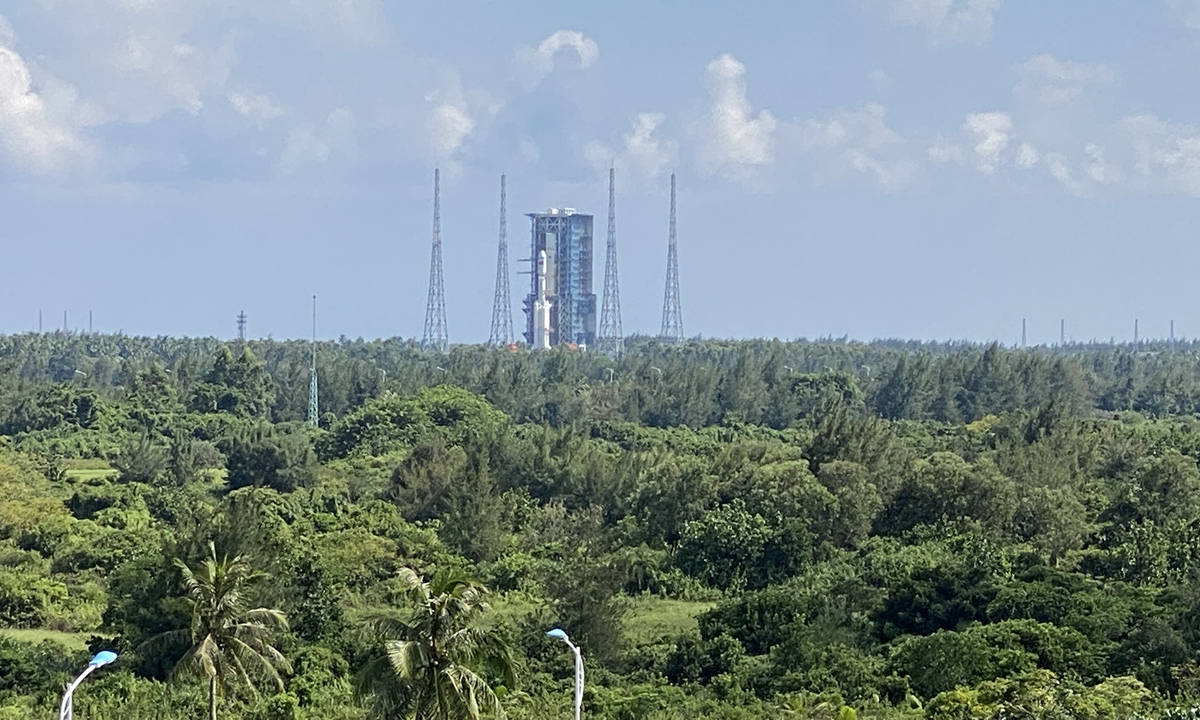
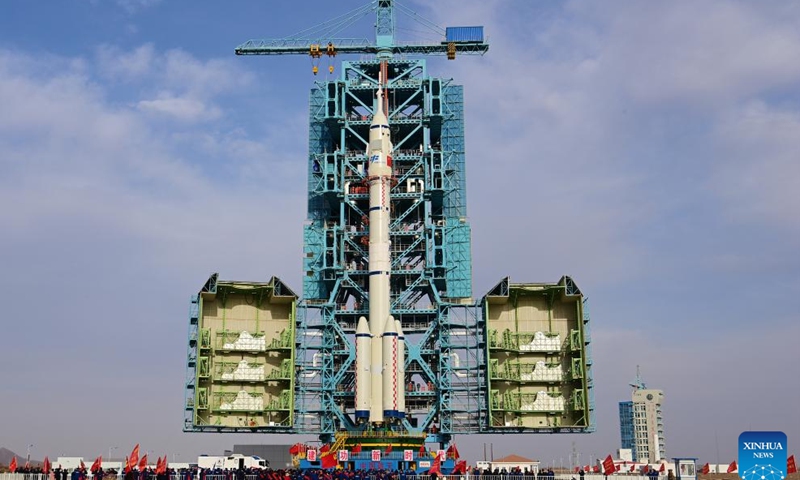
As the temperature drops to somewhere near minus 20 C in Jiuquan around this time of the year, the launch of Shenzhou-15, which is via a Long March-2F rocket from the Jiuquan center, also faces a special challenge of extremely low temperature.
According to the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology (CALT), the developer of the Long March-2F rocket, Shenzhou spacecraft had only been launched twice in unscrewed condition during the Shenzhou-1 and 4 missions in late November. Shenzhou-15 would be first one to be carried out with taikonauts onboard in the cold weather.
However, the CALT explained that they have taken such unique challenge into consideration. They have also confirmed the two sets of the temperature system inside the rocket's nose cone, to make sure that the temperature of the propellant of the return and propelling module meets the launch condition.
The line-up of three taikonauts for Shenzhou-15 manned spaceflight mission, Zhang Lu, Fei Junlong, and Deng Qingming (from left to right). Photo: VCG
China on Monday unveiled the line-up of three taikonauts for Shenzhou-15 manned spaceflight mission that is set to be launched on Tuesday night. The trio led by mission commander Fei Junlong with two space newcomers Deng Qingming and Zhang Lu are going to conduct a direct handover in orbit with the Shenzhou-14 crew at the China Space Station in construction, which shall mark a first in China's aerospace history.
The upcoming Shenzhou-15 crewed spaceflight mission is not only the anchor-leg launch mission at the China Space Station construction stage, but also is the first one to embark on the next operational stage, Fei, the 57-year-old veteran taikonaut who visited the space as the mission commander in the China's Shenzhou-6 mission in 2005, remarked at a press conference on Monday at the Jiuquan Satellite Space Launch Center in Northwest China's Gansu Province.
The crew will carry out more experiments in orbit, operate, maintain and repair relevant equipment and above all execute even more challenging extravehicular activities, or known as spacewalks, with more complicated paths to take on, Fei said on Monday.
The Shenzhou-15 crew has undergone great amount of specific training, which made them very confident to deliver all the set goals and to successfully complete their space run, Fei said.
Deng Qingming, 56, is among the first batch of taikonauts trained in China that includes the country's first astronaut Yang Liwei and also his mission commander Fei in the Shenzhou-15 mission. He has served as a backup for nearly 25 years, in missions such as the Shenzhou-9 and 10, but never got the chance to fly. This will be his first time ever in space.
Zhang Lu, 46, also a new face, was selected in the second batch of taikonauts trained in China in 2010.
Mission insiders told the Global Times on Monday that the two crews of six taikonauts will carry out the space station handover in a face-to-face manner for the first time in the country's manned space history and that is not only of symbolic significance but also carries great practical values to the overall development of the country's first permanent space outpost.
Sources with China's astronaut training system, told the Global Times on Monday that such feat would enable the predecessor Shenzhou-14 to introduce and share what their work and life would be like inside the space station with the new Shenzhou-15 crew directly, boosting the continuity and efficiency of the handover.
It would also help save the resources to set the space station combo from occupied state to unoccupied one and then back again. And the handover will be more target-oriented, especially for those ongoing experiments and space station maintenance work, the sources said.
Having six taikonauts simultaneously onboard the China Space Station in construction, would also verify its performance under the full load condition, which would lay groundwork for future tasks where more payload technicians are needed for more complicated experiments, Song Zhongping, a space watcher and TV commentator, told the Global Times.
By plan, the handover will last for a week or so, and after that, Shenzhou-14 crew will return to the Dongfeng landing site on Earth.
As the temperature drops to somewhere near minus 20 C in Jiuquan around this time of the year, the launch of Shenzhou-15, which is via a Long March-2F rocket from the Jiuquan center, also faces a special challenge of extremely low temperature.
According to the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology (CALT), the developer of the Long March-2F rocket, Shenzhou spacecraft had only been launched twice in unscrewed condition during the Shenzhou-1 and 4 missions in late November. Shenzhou-15 would be first one to be carried out with taikonauts onboard in the cold weather.
However, the CALT explained that they have taken such unique challenge into consideration. They have also confirmed the two sets of the temperature system inside the rocket's nose cone, to make sure that the temperature of the propellant of the return and propelling module meets the launch condition.

China's Space Station is the first of its kind to be open to all UN member states. So far a number of science experiment projects from 17 countries including Switzerland, Poland, Germany and Italy have been included in the selected projects of China Space Station, Zhao said.
Related posts:
Shenzhou-14 spacecraft delivers three taikonauts to China Space Station to complete national space lab construction
CHINA ADDS SECOND SCIENCE LABORATORY TO ORBITING SPACE STATION
Mengtian lab module successfully launched, the final part of Chinese space station
China's cyberspace whitepaper highlights cooperation, 'fundamentally different' from US' proposition
Cooperation, decoupling, dysfunctional politics, hypocritical to worry about nuclear war?
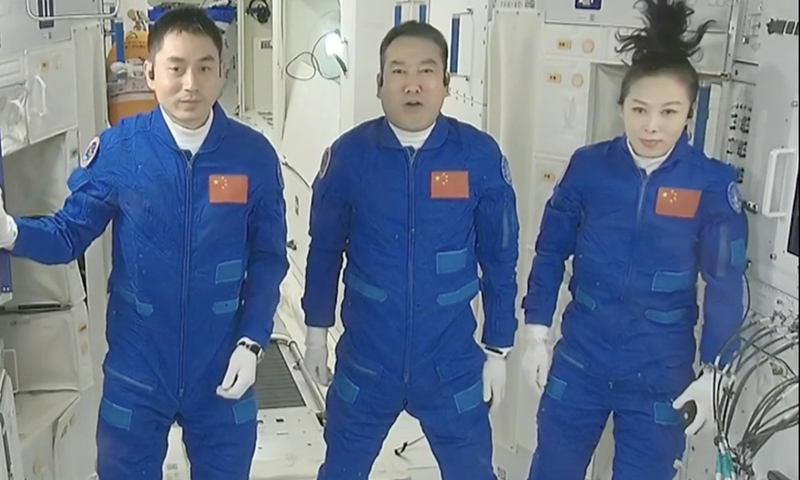



 Shenzhou-13 crew
Shenzhou-13 crew